WHAT IS TRANSCRANIAL MAGNETIC STIMULATION?
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (RTMS) is a type of therapy that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. Researchers disagree on why brain stimulation therapies are helpful for people with severe depression, but some believe it may have to do with a lower-than-normal amount of activity in the parts of the brain responsible for regulating mood. Deep brain stimulation activates these areas of the brain, making the symptoms of major depressive disorder more manageable.
Virtue Recovery Center provides residential addiction treatment as well as inpatient treatment for major depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other mental health conditions.
For patients with a major depressive disorder that hasn’t responded to antidepressant medications and other treatments, we offer transcranial magnetic stimulation using the NeuroStar device. Transcranial magnetic stimulation is one of several brain stimulation therapies used to treat the symptoms of major depression. Keep reading to learn more about this noninvasive, groundbreaking treatment.
FREE ASSESSMENT
Get immediate treatment help now. 100% safe & confidential.
CALL (866) 461-3339
Contact us to schedule a free confidential drug and alcohol assessment with a licensed clinician.
What Happens During a Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Session?
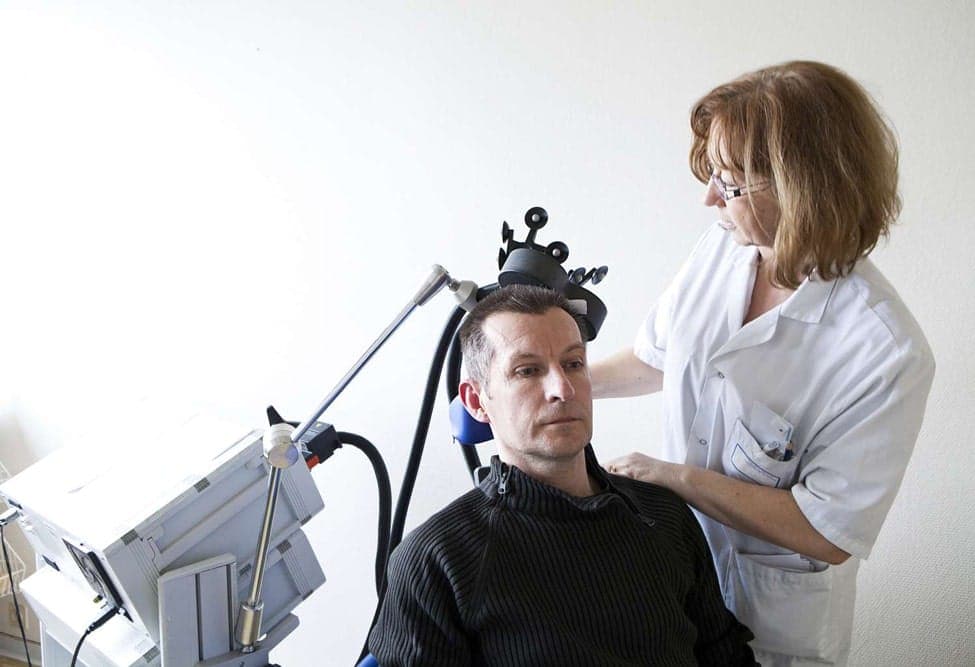
A transcranial magnetic stimulation session typically takes less than one hour to complete. Before the treatment session begins, you’ll recline in a chair so one of our treatment professionals can position a small, curved device on your head. The device contains an electromagnetic coil that produces the pulses used to stimulate certain parts of your brain.
When the treatment session begins, you’ll hear a clicking sound and then feel a tapping sensation on your head as the device delivers repetitive magnetic pulses. TMS requires no sedatives or anesthesia, so you won’t have to worry about feeling groggy or having an adverse reaction to any medications during your treatment. Because it’s a noninvasive form of treatment, there are no electrodes or implantable devices involved in transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Benefits of Brain Stimulation for Depression
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation has several key benefits for people suffering from treatment-resistant depression. One of the greatest benefits of TMS is improved mood regulation. People with depression often have difficulty regulating their emotions, causing mood swings that can make it difficult to maintain personal relationships. While some people with depression have persistent feelings of sadness, others are irritable, get frustrated easily or lash out in anger when their friends or family members ask what’s wrong. Repetitive TMS can reduce these mood swings, leaving people with depression feeling more confident and in control of their lives.
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation may also work when other depression treatments have failed. Antidepressants, cognitive behavioral therapy and other treatments all have their place, but they don’t work for everyone. Repetitive TMS gives patients with treatment-resistant depression the opportunity to control their symptoms without undergoing more invasive treatments.
Another benefit of repetitive TMS is that it’s a targeted therapy aimed at the specific parts of the brain implicated in serious cases of depression. Antidepressants treat depression symptoms, but they can also cause weight gain, dizziness, headaches, indigestion and other bothersome side effects. Because repetitive TMS uses a targeted magnetic pulse aimed directly at the head, it doesn’t produce systemic side effects that can make it difficult to stick with your treatment plan.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) vs Electroconvulsive Therapy
transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy is an option for some people who have severe depression and don’t want to try electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Although electroconvulsive therapy treats depressive symptoms, it’s very different from TMS. While TMS uses magnetic fields, ECT uses electrical pulses delivered via electrodes applied to the scalp. Before undergoing electrical stimulation to treat medication-resistant depression, a patient must have a thorough medical examination. Some patients even need to have their heart function checked to make sure they can do ECT safely. Because TMS is noninvasive, it doesn’t require as many precautions.
To have ECT, a patient must undergo general anesthesia, which has serious risks. These risks are even more concerning for people with diabetes, heart disease and other chronic health conditions, as undergoing general anesthesia may increase the risk of stroke or heart attack or cause the patient to develop pneumonia as a result of being intubated. TMS doesn’t require anesthesia, so you can return to your normal activities as soon as your session ends. Any side effects of TMS are generally mild and limited to your head and facial muscles.
Many people don’t realize that the electrical impulses delivered during an ECT session cause small seizures within the brain. As a result, ECT can result in short-term memory loss or make it difficult for patients to learn new things. In severe cases, ECT patients develop long-term memory problems. TMS is noninvasive and doesn’t cause any seizure activity, so there’s no risk of memory loss or learning difficulties.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) vs Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is also used to treat depression. VNS requires a surgical procedure to implant a small device in the chest. The device delivers targeted electrical impulses to the vagus nerve; those impulses are then transmitted to the brain to treat the symptoms of depression. Researchers don’t know why VNS is effective for treating depression, but they believe the electrical impulses reach the brain cells involved in regulating a person’s mood.
When compared to VNS, one of the main benefits of TMS is that it’s a noninvasive procedure. You don’t have to undergo surgery or have a medical device implanted in your body, shielding you from many of the risks of VNS treatment. Another advantage of TMS over VNS is that you don’t have to worry about whether an implanted device will prevent you from having other medical procedures. Because VNS uses an implantable device, patients may not be able to undergo magnetic resonance imaging. The VNS device can also make it more difficult to get a mammogram or undergo emergency treatment for cardiac arrest.
BENEFITS OF NEUROSTAR VS OTHER TMS DEVICES
Virtue Recovery Center chose the NeuroStar device for its precision and simple design. Unlike other transcranial magnetic stimulation devices, NeuroStar doesn’t require a mouth guard, headgear or any other equipment that can make you uncomfortable. Patients with claustrophobia are likely to tolerate NeuroStar better than other devices because they aren’t surrounded by intrusive equipment during their treatment sessions.
The NeuroStar device also has built-in technology to ensure you get the full benefits of each treatment. This technology ensures the device is positioned correctly, measures the magnetic field level and ensures you receive the full dose during every session. Many of our patients also appreciate that the NeuroStar device is manufactured in the United States and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
EFFECTIVENESS OF TMS FOR SEVERE DEPRESSION
Depression is one of the most common mental health disorders, affecting up to 5% of adults worldwide. Although medications can be helpful, not everyone responds to them in the same way, leaving many people in search of more effective treatment options. Transcranial magnetic stimulation produces a meaningful response in 50% to 60% of people who try it after having no response to antidepressants. About 33% of those people go into full remission, meaning that TMS keeps their depression symptoms at bay for long periods of time.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)
It depends on your symptoms and how well you’re responding to the treatment. Many patients report significant improvement in their depression symptoms after four to six weeks of treatment with the NeuroStar TMS device. Although some patients report that NeuroStar controls their symptoms for 12 months or longer, you may need occasional maintenance treatments. Your treatment provider will determine how many sessions you need and how long each session should last.
TMS isn’t a first-line treatment for depression, so it’s not something you can do until you’ve tried other options and discovered they don’t work for you. Your doctor may recommend that you take antidepressants or try several types of therapy, including cognitive behavioral therapy and psychotherapy, before considering TMS.
Although TMS is safe for most people, it’s not recommended for people with a history of certain medical conditions or surgical procedures. For example, you shouldn’t try TMS if you have any nonremovable metal in your head or neck. This includes shrapnel in your skull, metal-containing implants in your ears, metal clips used to repair an aneurysm in the brain or stents in any of the blood vessels above your shoulders. You should also avoid TMS if you have a deep brain stimulator or electrodes implanted in your brain.
FIND OUT IF TMS IS RIGHT FOR YOU
If you haven’t been able to manage your depression with medications or therapy, TMS may be an option. Although Virtue Recovery Center offers addiction treatment, you don’t need to have a substance use disorder to benefit from our TMS offerings. We are transcranial magnetic stimulation providers and also offers other services as stand-alone treatments for people with depression, anxiety, PTSD and other mental health disorders. To regain control of your life, call 866-558-1376 or contact us online.

