Seeking Treatment for Alcoholism (Alcohol Use Disorder)
15 min read
Alcoholism Treatment Options #
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is not just a personal struggle; it’s a global health crisis that silently weaves through societies, affecting millions of lives across every continent. With a staggering 80% of people worldwide having consumed alcohol in their lifetime, and an average of 8.6% living with AUD, the scale of this issue is both vast and deeply personal 5.
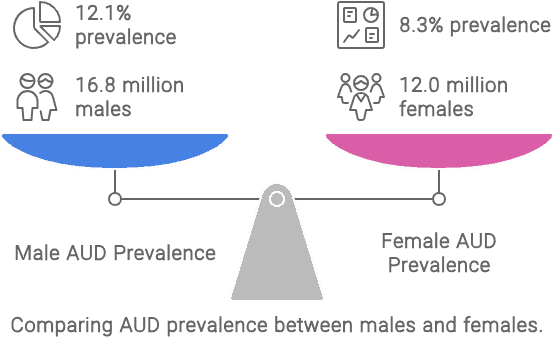
Data Source: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42728/NSDUHDetailedTabs2022/NSDUHDetailedTabs2022/NSDUHDetTabsSect5pe2022.htm#tab5.9a
Treatment Process #
The treatment process for AUD involves several key steps, tailored to individual needs. Initially, a comprehensive assessment of a person’s alcohol problems and complications guides the selection of the appropriate level of care. The four basic levels of care, as defined by the American Society of Addiction Medicine, range from outpatient services, which allow individuals to maintain their regular routines, to intensive inpatient programs that provide medically-directed 24-hour services, including withdrawal management1.
Medications #
Medications play a crucial role in the treatment of AUD by helping to stop or reduce drinking and prevent relapse. Healthcare professionals can prescribe non-addicting medications as part of the treatment plan. The main medications used in the treatment of alcoholism include:
- Naltrexone: Reduces the urge to drink.
- Acamprosate: Helps restore the brain’s chemical balance in individuals who have stopped drinking.
- Disulfiram: Causes unpleasant effects when alcohol is consumed, acting as a deterrent to drinking 1.
These medications can be used alone or in combination with therapy approaches, depending on individual needs and treatment plans.
Therapy Approaches #
Therapy is a cornerstone of alcoholism treatment, providing individuals with coping strategies and skills to stop or reduce drinking. Therapy can take place in one-on-one, family, or group sessions and includes various approaches:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Focuses on identifying and changing negative thoughts and behaviors related to alcohol use. CBT helps individuals develop coping strategies and skills to deal with situations that might trigger drinking 2 5.
- Motivational Interviewing (MI): A counseling approach that enhances motivation to change drinking behavior by helping individuals resolve ambivalence about entering treatment and stopping drinking 4.
- Family/Couple’s Therapy: Involves therapy sessions that may include family members or partners to address and improve the dynamics that may contribute to alcohol use 4.
These therapy approaches can be delivered in various settings, including in-person and through telehealth services, allowing for flexibility in how individuals receive treatment. The choice of therapy approach is tailored to the individual’s specific needs, preferences, and situation 1 2.
In conclusion, the treatment of alcoholism involves a combination of professionally led treatment options, including therapy approaches and medications, tailored to individual needs. The treatment process begins with a comprehensive assessment to guide the selection of the appropriate level of care and may include outpatient services, telehealth, or inpatient programs. Therapy approaches like CBT, MI, and family therapy play a crucial role in providing individuals with the skills and strategies needed to overcome alcoholism 1 2 5.
Supporting a Loved One with Alcoholism #
Supporting a loved one struggling with alcoholism can be challenging, but it’s crucial for their recovery journey. Understanding how to effectively support them, while also taking care of your own well-being, is essential. Here are some strategies to consider:
Having Productive Conversations #
Initiate open, honest, and non-judgmental conversations about their drinking behavior and its effects. Express your concerns and the impact of their alcohol use on you and others, emphasizing your support for their recovery.
Avoiding Enabling Behaviors #
It’s important to recognize and avoid actions that may inadvertently enable your loved one’s alcoholism. This includes making excuses for their behavior, covering up their drinking, or taking on their responsibilities. Setting boundaries is crucial for both your well-being and their path to recovery.
Self-Care for Family and Friends #
Supporting someone with alcoholism can be emotionally draining. Prioritize your own mental and physical health by setting boundaries, seeking support for yourself, and engaging in activities that replenish your energy and resilience.
Support Resources #
Encourage your loved one to seek professional help and explore treatment options. Additionally, consider joining support groups like Al-Anon, which offer guidance and support for families and friends of alcoholics. These groups can provide a sense of community and shared experience that is invaluable during this challenging time.
Virtue Recovery Center #
As part of exploring treatment options for your loved one, consider Virtue Recovery Center, a reputable facility known for its comprehensive approach to treating alcoholism. Virtue Recovery Center offers a range of services tailored to meet individual needs, including detoxification, therapy, and aftercare planning. Their experienced team of professionals is dedicated to providing compassionate care and support, not only to individuals struggling with alcoholism but also to their families. By focusing on holistic recovery, Virtue Recovery Center aims to address the root causes of alcoholism and equip individuals with the tools they need for long-term sobriety.
Supporting a loved one with alcoholism requires patience, understanding, and a commitment to their well-being. By engaging in productive conversations, avoiding enabling behaviors, taking care of your own health, and utilizing resources like Virtue Recovery Center, you can provide meaningful support that encourages recovery and fosters a healthier future for everyone involved.
Prevention Programs and Initiatives #
Preventing alcoholism involves a multifaceted approach that includes education, community involvement, and policy initiatives. These efforts aim to reduce alcohol abuse and its related problems by addressing the issue from various angles.
School-Based Alcohol Education #
Schools play a critical role in preventing alcohol use among youth. Effective school-based alcohol prevention programs are designed to educate students about the risks associated with alcohol use and to develop skills to resist peer pressure. These programs often incorporate interactive teaching methods, involve peer leaders, and are integrated into the broader school curriculum. Research has shown that to be most effective, interventions should be theory-driven, address social norms around alcohol use, and be culturally and developmentally appropriate 11 13.
Community Coalitions #
Community coalitions are alliances that bring together various sectors of a community, such as schools, law enforcement, healthcare, and local government, to work towards reducing alcohol abuse. These coalitions implement strategies tailored to their community’s specific needs, focusing on changing social norms, developing new policies, and supporting evidence-based prevention programs. CADCA (Community Anti-Drug Coalitions of America) represents over 5,000 community coalitions worldwide, demonstrating the effectiveness of collective action in fostering drug-free communities 12.
Policy Approaches #
Policy interventions can significantly impact alcohol consumption patterns and related harms. These include regulating alcohol marketing, implementing taxes on alcoholic beverages, and enforcing laws to reduce drunk driving. Restrictions on alcohol advertising, for example, aim to limit the exposure of children and adolescents to marketing that promotes alcohol use. Such policies can help shift community norms and reduce underage drinking. Studies have shown that comprehensive policy approaches, including advertising restrictions and pricing strategies, can effectively reduce alcohol consumption and its negative consequences 10 13.
Prevention programs and initiatives play a vital role in reducing alcohol abuse and its associated harms. By educating youth, mobilizing communities, and implementing effective policies, it is possible to create healthier environments that discourage alcohol abuse and support individuals in making informed choices about alcohol use.
Self-Help Strategies for Sobriety #
Maintaining sobriety can be a challenging journey, but there are several self-help strategies that individuals can employ to support their recovery. These strategies can empower individuals to take control of their sobriety and build a fulfilling life free from alcohol.
Building a Sober Support Network #
A sober support network is a group of individuals who provide encouragement and understanding to someone in recovery. This network can include friends, family members, professionals, and peers in recovery. A strong support network can help individuals remain focused on their recovery goals and provide a sense of community. Regular engagement with a support network, such as attending meetings, having a sponsor, and participating in sober activities, can significantly increase the chances of long-term recovery 15 16.
Alternative Coping Strategies #
Developing healthy coping strategies is essential for managing the stressors and triggers that can lead to relapse. Alternative coping methods can include stress and anger management techniques, communication skills, and relapse prevention tools. Engaging in hobbies, exercise, and other fulfilling activities can also serve as positive outlets. It’s important to acknowledge the benefits of using substances in the past, such as relaxation or escape, to understand the importance of finding healthy alternatives that provide similar benefits without the negative consequences 15.
Self-Monitoring Tools (apps, journals, etc.) #
Self-monitoring tools such as apps and journals can help individuals track their progress, manage triggers, and maintain accountability. These tools can provide reminders, motivational messages, and track milestones in recovery. They can also facilitate self-reflection, helping individuals to recognize patterns in their behavior and make adjustments as needed. Studies have shown that using smartphone apps for self-monitoring and recovery support can be an effective component of a comprehensive recovery plan 17 18.
Incorporating these self-help strategies into daily life can enhance an individual’s ability to maintain sobriety. By building a strong support network, employing alternative coping strategies, and utilizing self-monitoring tools, individuals in recovery can create a solid foundation for a sober and healthy lifestyle.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailoring Recovery to Individual Needs #
The journey to recovery from alcohol use disorder (AUD) is as unique as the individuals who embark on it. Recognizing this, healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of personalized treatment plans, which are tailored to meet the specific needs, preferences, and situations of each person. This individualized approach not only enhances the effectiveness of treatment but also empowers individuals in their recovery process.
The Foundation of Personalized Treatment: Comprehensive Assessment #
A comprehensive assessment by healthcare professionals is the cornerstone of creating an effective personalized treatment plan. This assessment evaluates the severity of the AUD, any co-occurring mental health disorders, and the individual’s social, psychological, and medical background.
Based on this assessment, professionals can guide individuals towards the most appropriate treatment modalities, whether it be outpatient services, intensive inpatient programs, or a combination of therapies and medications.
Examples of Personalized Treatment Approaches #
- Outpatient vs. Inpatient Care: Depending on the assessment, some individuals may benefit from outpatient services that allow them to maintain their daily routines while receiving treatment. Others may require the structured environment of an inpatient program to manage withdrawal symptoms and receive 24-hour care19.
- Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT): Medications such as Naltrexone, Acamprosate, and Disulfiram can be prescribed based on individual health profiles and specific needs. For example, Naltrexone is often used to reduce the urge to drink, making it a suitable option for those struggling with cravings19.
- Therapy Approaches: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Motivational Interviewing (MI), and Family/Couple’s Therapy are tailored to address the unique challenges faced by the individual. CBT may be recommended for those who need to develop coping strategies, while MI could be more effective for individuals uncertain about change19.
The Role of Technology in Personalized Plans #
Modern technology, including telehealth services and eHealth tools, offers additional flexibility in creating personalized treatment plans. Telehealth can provide access to therapy and medical care through phone or video sessions, ideal for those with scheduling constraints or who prefer maintaining privacy. eHealth tools, including digital self-help programs and mobile apps, support individuals in managing their recovery process, offering a personalized approach to prevent relapse19.
Effectiveness of Personalized Plans #
The effectiveness of personalized treatment plans lies in their ability to address the multifaceted nature of AUD. By considering the individual’s entire context — including their psychological, social, and biological factors — personalized plans can significantly improve the chances of successful recovery. Studies have shown that when treatment is tailored to an individual’s specific needs, it leads to better engagement, higher satisfaction with treatment, and, most importantly, improved outcomes19.
In conclusion, personalized treatment plans represent a cornerstone of effective AUD treatment, reflecting a shift towards more holistic and individual-centered care. By leveraging comprehensive assessments, a range of treatment options, and the latest technology, healthcare professionals can design treatment plans that truly resonate with the needs of those they aim to help. This personalized approach not only enhances the effectiveness of treatment but also empowers individuals on their journey to recovery.
Conclusion #
In conclusion, overcoming alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a journey that requires courage, commitment, and the right support. The path to recovery is not one-size-fits-all; it is a deeply personal process that necessitates a tailored approach, considering the unique needs and circumstances of each individual. From the initial comprehensive assessment to the selection of therapy approaches and the integration of medications, each step is crucial in crafting a treatment plan that offers the best chance for success. Moreover, the importance of a supportive network—whether through professional help, family, or peer groups—cannot be overstated, as it provides the strength and encouragement needed to navigate the challenges of recovery. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness. With the right treatment and support, individuals struggling with AUD can reclaim their lives, one step at a time.
FAQ: #
Q: What is alcoholism? #
A: Alcoholism, also known as alcohol use disorder, is a chronic disease characterized by a strong craving for alcohol, continued use despite harmful consequences, and the inability to control drinking.
Q: How do I know if I have alcoholism? #
A: Some signs of alcoholism include an inability to limit drinking, experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not drinking, neglecting responsibilities because of alcohol, and an increasing tolerance to alcohol.
Q: What are the treatment options for alcoholism? #
A: Treatment for alcoholism can include therapy, medications, support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous, and residential treatment programs in rehab centers.
Q: How can I seek treatment for alcoholism? #
A: If you or a loved one is struggling with alcoholism, you can start by reaching out to a treatment provider or rehab center specialized in alcohol addiction to explore the available options for treatment.
Q: What is alcohol withdrawal and how is it treated? #
A: Alcohol withdrawal is a set of symptoms that occur when a person who is dependent on alcohol suddenly stops drinking. It can be dangerous and should be managed by medical professionals in a treatment program or rehab center.
Q: How can therapy help in treating alcoholism? #
A: Therapy can help individuals with alcoholism identify and address underlying issues that contribute to their drinking, develop coping mechanisms, and learn strategies to prevent relapse.
Q: What are the benefits of joining a support group for alcoholism? #
A: Support groups provide a sense of community, understanding, and accountability. They offer a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, receive encouragement, and build a network of support during their recovery journey.
Q: How can I help a loved one who is struggling with alcoholism? #
A: You can support your loved one by encouraging them to seek professional treatment, attending therapy or support group sessions with them, showing empathy and understanding, and helping them make positive lifestyle changes.
References: #
-
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. (n.d.). Types of alcohol treatment. https://alcoholtreatment.niaaa.nih.gov/what-to-know/types-of-alcohol-treatment
-
AlcoholRehabGuide.org. (n.d.). Types of therapy for alcoholism. https://www.alcoholrehabguide.org/treatment/types-therapy-alcoholism/
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (n.d.). SAMHSA’s National Helpline. https://www.samhsa.gov/find-help/national-helpline
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. (n.d.). Recommend Evidence-Based Treatment: Know the Options. https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/health-professionals-communities/core-resource-on-alcohol/recommend-evidence-based-treatment-know-options
- Glantz, M. D., Bharat, C., Degenhardt, L., Sampson, N. A., Scott, K. M., Lim, C. C. W., Al-Hamzawi, A., Alonso, J., Andrade, L. H., Cardoso, G., De Girolamo, G., Gureje, O., He, Y., Hinkov, H., Karam, E. G., Karam, G., Kovess-Masfety, V., Lasebikan, V., Lee, S., Levinson, D., … WHO World Mental Health Survey Collaborators (2020). The epidemiology of alcohol use disorders cross-nationally: Findings from the World Mental Health Surveys. Addictive behaviors, 102, 106128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106128 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7416527/
- UpToDate. (n.d.). Alcohol use disorder: Pharmacologic management. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/alcohol-use-disorder-pharmacologic-management
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Alcohol use disorder – Diagnosis and treatment. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/alcohol-use-disorder/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20369250
- American Academy of Family Physicians. (2016). Medications for Alcohol Use Disorder. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2016/0315/p457.html
- WebMD. (n.d.). Treatment of Alcohol Abuse & Alcoholism. https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/addiction/alcohol-use-disorder-treatments
- Babor, T. F., Robaina, K., Noel, J. K., & Ritson, E. B. (2017). Vulnerability to alcohol-related problems: A policy brief with implications for the regulation of alcohol marketing. Annual Review of Public Health, 38, 81-104. https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040617-014711
- Hingson, R., & White, A. (2014). New research findings since the 2007 Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent and Reduce Underage Drinking: A review. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 75(1), 158-169. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3860568/
- Rural Health Information Hub. (n.d.). Community coalitions to prevent substance abuse. https://www.ruralhealthinfo.org/toolkits/substance-abuse/2/prevention/community-coalition
- Prevention First. (n.d.). Alcohol advertising restrictions. https://www.prevention.org/alcohol-policy-resource-center/fact-sheets/alcohol-advertising-restrictions/
- County Health Rankings & Roadmaps. (n.d.). Universal school-based alcohol prevention programs. https://www.countyhealthrankings.org/strategies-and-solutions/what-works-for-health/strategies/universal-school-based-alcohol-prevention-programs
- Melemis S. M. (2015). Relapse Prevention and the Five Rules of Recovery. The Yale journal of biology and medicine, 88(3), 325–332. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4553654/
- BlueCrest Recovery Center. (n.d.). How to build a sober support network. Retrieved from https://www.bluecrestrc.com/how-to-build-a-sober-support-network/
- Scott, C. K., Dennis, M. L., & Gustafson, D. H. (2017). Using smartphones to decrease substance use via self-monitoring and recovery support: study protocol for a randomized control trial. Trials, 18(1), 374. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-017-2096-z https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5553728/
- World Health Organization. (n.d.). Self-help strategies for cutting down or stopping substance use (ASSIST). https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789241599405
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. (2022, May 6). Recommend evidence-based treatment: Know the options. https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/health-professionals-communities/core-resource-on-alcohol/recommend-evidence-based-treatment-know-options




